Listed below are some typical security implementations in Servoy applications.
Basic Servoy Security
Practical where the security will be managed by the developer of the application and does not require anyone else configuring users or permissions.
Steps
- Using the User/Group editor, decide what authorization permission groups are required for the application. Create these groups before development begins.
- During development of tables and forms, use the settings on the security tab of each editor to configure what permissions each group has for the table/form. Keep in mind during form development that elements must be named in order to assign permissions.
- Set the mustAuthenticate flag to true (selected) for the solution.
- Create users with either the User/Group editor or with the Users page in the application server administration utility. Assign users to groups in either editor.
- Deploy the application. When launching the application, the default login window will appear to authenticate the user.
Custom Authentication
To allow tenant administrators or "super users" to adminstrate users, or if you are using an external authentication source, you must create custom authentication. Custom authentication will allow the developer to use a users table in the database for authentication or access an external authentication directory
NOTE: To use external authentication, most likely a plugin is required.
Steps
- If using Servoy for storing user data, create a user database for the application or set of applications. Be sure to at least include a username and password column in the database.
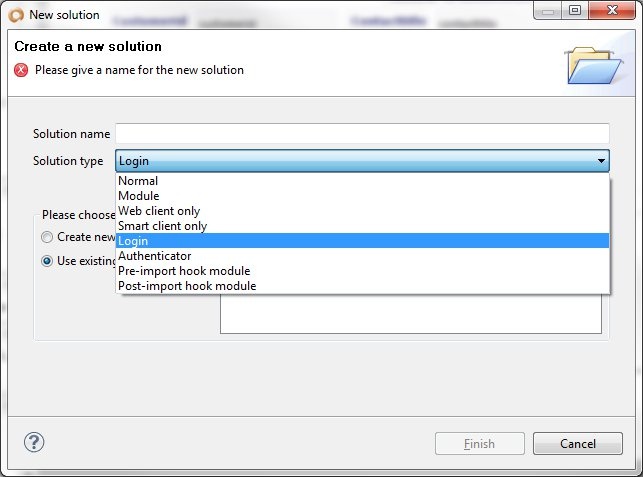
- Create a login solution. A login solution should have the following attributes:
- Solution type of login
- A login form set as the first form.
- The login form should have fields (normally form variables) for entering a username and password
- A button or method that will validate the fields are not null and finally call the authentication method of the authenticator solution. See Login Solution Example.
- The login solution has no database access, so if there is any validation done during the login process (find tenant id, verify user exists, etc.), the login solution must call an authenticator solution for any database information.
- Solution type of login
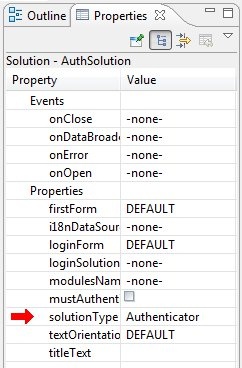
- Create an authenticator solution (during the solution creation process, same as login solution). The authenticator has the following attributes:
- Solution type of authenticator
Overview
Content Tools
Activity